Can you explain more about the purposes and the methods of FMEA?

When we do FMEA, we need to consider the expected failures which may be caused by whatever changes, such as equipment, people, methods or environment. Because if the causes change, the expected failures also change.

According to FMEA method, we have to anticipant the cause of failures with “Failure mode” and “effect of failure mode” in order to prevent troubles.

What is “Failure mode“? What is the difference between “Failure mode” and “Failure“?

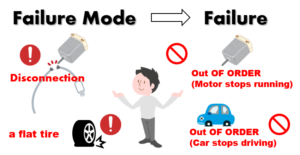
“Failure Mode” means “Manner in which an item fail”, and “Failure” means “Loss of function”.
For example:
- “Failure Mode“: Disconnection of cables =>”Failure“:Motor stops running
- “Failure Mode“: Have a flat tires => “Failure“:Car stops driving

I see.

In manufacturing industry, there are roughly 2 types of FMEA, Design-FMEA and Process-FMEA.

What the difference between Design-FMEA and Process-FMEA?

- Design-FMEA (D-FMEA) : FMEA related to Design
- Process-FMEA (P-FMEA) :FMEA related to Process
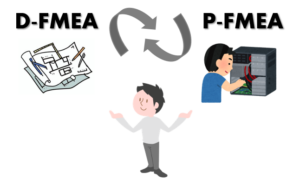

When we make a product, we need to consider expected failures from not only Design point of view, but also from manufacturing process point of view. Thus, it is very important to connect D-FMEA and P-FMEA.

I see. I understand that FMEA helps us design products and processes with high reliability (= don’t often break down or get trouble).

So, can you tell me how to do FMEA?

In FMEA, we quantify the risks (RPN*) determined by multiplying the rating for the three factors (severity x frequency x detection). This helps us prioritize the risks.
*RPN : Risk Priority Number

① Input the Failure Mode (Expected manner which an item fails)
② Input the Impact of this Failure Mode on Product or Customer
③ Rate on a scale of 1 to 10: Severity of the impact.
④ Input the potential causes of failure.
⑤ On a scale of 1 to 10: Frequency of failure
⑥ Input the method (test method) to detect failure
⑦ On a scale of 1 to 10: Detection rate with each test method.
⑧ Calculate Risks (RPN) by Severity③×Frequency⑤×Frequency⑦

I see. Those above steps makes us possible to quantify the risks (RPN), right !?

Yes!!
After that, we try to reduce the risks through these steps ⑨ and ⑩.
⑨ For items with high risks (RPN), input improvement plan to reduce Risks.
⑩ Calculate risks (RPN) after the improvement.

Step ① and ② are specifically important. Because it is said that if we can raise expected risks more, we can do FMEA better with quality.

I understand that we can reduce risks (RPN) in FMEA by reducing “Frequency” and “Detection“.
*RPN: the less, the better

That’s right!
By the way, IATF16949 requires us to review documents periodically as a corrective action in case failure occurs. It’s important to reduce Risks with FMEA.

When we develop the next model, we usually refer FMEA for the previous model to prevent recurrence of failure. (We usually add new items to FMEA for the previous model.)

I see.
It takes time to do FMEA, but once we complete it with one model, then we can leverage it for the next model as well!!

NSS offers [APIS IQ] software which is the reference product in the field of FMEA and Risk Analysis.
Click HERE to learn about [APIS IQ].