1」

Hello. I have a small question. I recently read the article 1/2: What Is VDI ~ How does it benefit your organization? ~ and I’m wondering why a GPU is required when using VDI for CAD work.

Hello. Thank you for your question.

Today, I’d like to explain how VDI can be used in conjunction with CAD workloads.
Let me start by explaining why GPU is required for CAD work or CATIA usage.
CATIA and other CAD/CAE software require very high graphics processing power. They are used for rendering 3D models, rotating parts in real time, and opening large assembly files.
GPU is essential for CAD on VDI. Without it, performance is laggy.
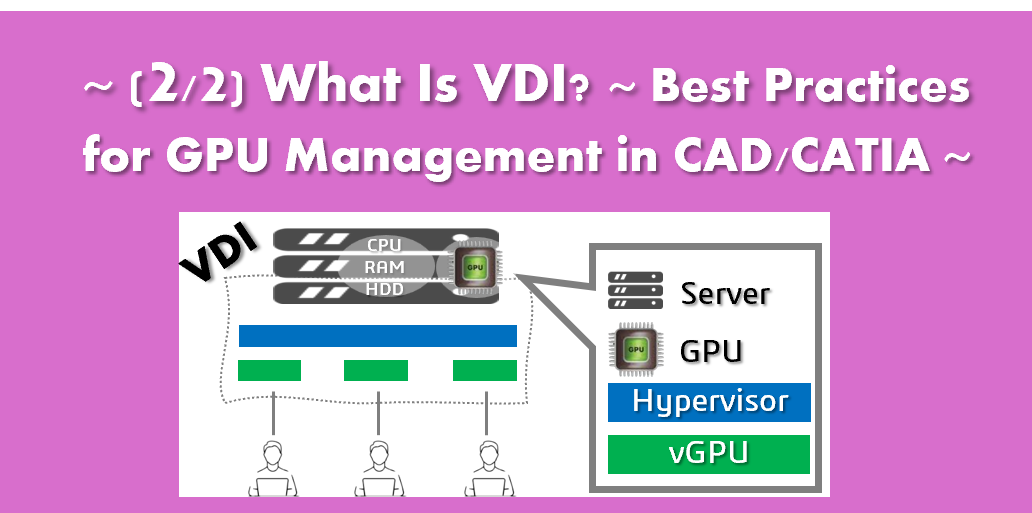
A virtualization-capable GPU is required to allocate resources to each VM.
What’s GPU?
What’s GPU?
– A GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is a processor specialized in handling 2D and 3D graphics processing. It is essentially the “brain” inside a computer that is dedicated to drawing images and designs.
CAFor applications such as CAD, CAM, and CATIA, a GPU enables:
- Stable and consistent display performance
- Smooth rotation of 3D models
- Fast loading of large 3D files

I’ve heard the phrase “assigning a GPU to each VM.” What does that actually mean?

In simple terms, it means that when multiple users share a single physical GPU, each user is allocated a fixed portion of the GPU’s performance.
This ensures that your CAD work is not affected by what other users are doing, and you always get stable, predictable performance.

I see.
So how is the GPU shared among multiple VMs?

GPU sharing is achieved using NVIDIA vGPU (Virtual GPU) technology.
Enterprise-grade GPUs such as NVIDIA L4, A16, A40, L40, and GRID/Tesla can be divided into multiple virtual GPUs. These virtual GPUs are then securely and efficiently assigned to multiple virtual machines (VMs).
Each VM behaves as if it has its own dedicated GPU, allowing users to work without being impacted by other users’ workloads.
What is VRAM?
VRAM is..
- RAM:A general-purpose memory used by the entire computer to run the operating system and applications.
- VRAM:A dedicated memory used specifically for display and 3D graphics processing.
VRAM stores the data that is actively being displayed and manipulated on the screen, such as 3D model geometry, textures, and rendering information used by CATIA.
vGPU / VRAM Allocation Guidelines
What is vGPU / VRAM allocation?
vGPU / VRAM allocation refers to a mechanism in which a single physical GPU is virtually partitioned, and GPU performance and VRAM capacity are allocated to each virtual desktop (VM).
This allows:
- Each VM to operate as if it has its own dedicated GPU and VRAM
- Stable performance that is not affected by other users
- Smooth and reliable 3D work for applications such as CAD and CATIA
=====================
Recommended vGPU / VRAM Allocation
① Small to medium assemblies (approx. 200–500 parts)
- 4–8 GB VRAM per VM
- Smooth interaction and stable display performance
② Large assemblies (1,000–5,000 parts)
- 8–16 GB VRAM per VM
- Insufficient VRAM may cause delays during rotation and zooming
③ Analysis, simulation, and rendering
- 16 GB VRAM or more, or full GPU allocation
- Heavy use of GPU computation and memory
=====================
What happens when VRAM is insufficient?
When VRAM is not enough, the following issues may occur:
- Choppy or laggy model manipulation
- Slow loading times
- Re-rendering delays when changing viewpoints
- OpenGL / DirectX errors
- CATIA crashes
This is because, when VRAM is exhausted, processing is offloaded to system RAM or disk storage, which is significantly slower than GPU memory.

If the server goes down during large-scale CATIA work, will the work be lost?

Yes, that risk does exist.
If a server failure occurs, work will stop immediately, and any unsaved data may be lost.
That’s why many companies implement an HA (High Availability) cluster.

So there is a risk of data loss.
What exactly is an HA cluster, and why is it important for CAD environments?

HA cluster is a system in which multiple servers are configured as a single group.
If one server fails, processing is automatically taken over by another server.
In CAD environments, this helps to:
- Minimize work interruptions
- Avoid reloading large assemblies
- Reduce the risk of data loss

I see.
So if we want to use CATIA seriously in a VDI environment, both GPU and HA are necessary, correct?

Yes. Especially for large-scale CAD/CAE environments, we strongly recommend having both.
Key Takeaways
1)GPU = Performance
- Without a GPU → Sluggish performance and frequent errors
- With the right GPU → Fast rendering, smooth operation, and stable performance
2)VDI = Flexible Workstyle
- The same work environment from anywhere
- No need for expensive workstations
- Business continuity from any device
3)HA Cluster = Design Continuity
- Downtime equals cost
- Without HA → Recovery delays and work interruptions
- With HA → Automatic restart in seconds and rapid return to work

That was very clear.
I didn’t realize how important GPU and HA are when using CATIA on VDI. Thank you.

NSS can help you select the right GPU, design the appropriate vGPU sizing, and propose an optimized overall VDI architecture.